A deep learning project focused on recognizing human emotions from speech. By systematically experimenting with various neural network architectures and employing advanced data augmentation, we developed a Bidirectional LSTM model that achieved 72% accuracy on the RAVDESS dataset, significantly outperforming other models and setting a new benchmark for our research.
- ContributionModel Development, Data Augmentation, Feature Extraction, Literature Review
- StackPython, TensorFlow, Keras, Scikit-learn, Librosa, NumPy
- Githubspeech-emotion-recognition
- PresentationView Presentation
Project Overview
The objective of this project was to build and train a neural network to classify human speech data by emotion. We used the audio-only portion of the RAVDESS dataset. The project was divided into several milestones: literature review, data collection and analysis, data augmentation, feature extraction, model building, and evaluation.
Data Processing & Feature Extraction
A key part of the project was careful data handling. We augmented the initial 1,440 audio files to a robust dataset of 12,000 files by adding noise, stretching, shifting, and changing pitch. This 8-fold increase in data was a major factor in our model's success. For feature extraction, we chose Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCCs), extracting 40 coefficients per file to capture the essential characteristics of the speech signals.
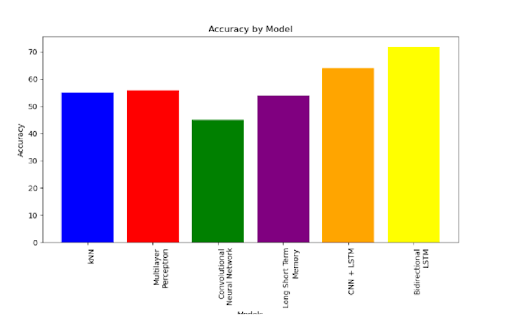
Model Exploration and Results
We built and evaluated six different models to find the best architecture for this task. The performance of each model is as follows:
- k-Nearest Neighbors: 55% accuracy (baseline)
- Multilayer Perceptron (MLP): 56% accuracy
- Convolutional Neural Network (CNN): 45% accuracy
- Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM): 54% accuracy
- Hybrid CNN+LSTM: 64% accuracy
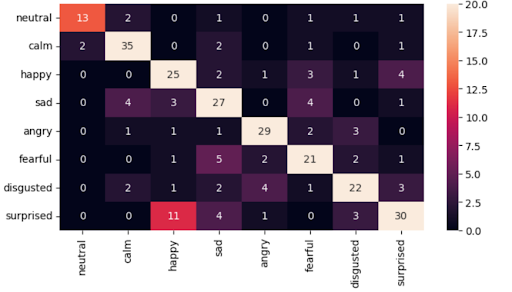
- Bidirectional LSTM: 72% accuracy (best performing)
Our findings showed that the Bidirectional LSTM outperformed all other models. We hypothesize that its ability to process sequences in both forward and backward directions allows it to capture more contextual information from the audio, leading to a more accurate emotion classification. The hybrid CNN+LSTM also showed promise, effectively combining the spatial feature extraction of CNNs with the temporal modeling of LSTMs.